(Image source: Angelw. Chem. Int. Ed.)
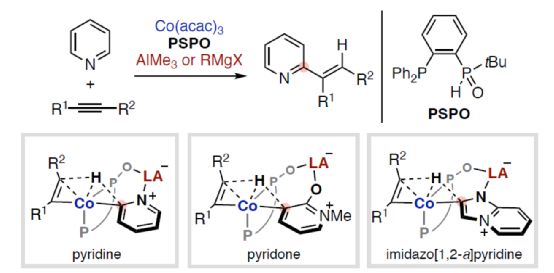
The synergy between electron-rich transition metals (TM) and Lewis acid (LA) main group metals has developed into a unique and useful concept, which can be used for the activation and transformation of inactive chemical bonds containing Lewis basic sites. In particular, the reactivity and selectivity can be enhanced by using properly designed bifunctionalized ligands to coordinate TM and LA (Scheme 1). Nakamura research group (J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 17978; J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 9590; Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 3316.) found that hydroxyphosphine ligands can accelerate the cross-coupling reaction between nickel-catalyzed inactive aryl fluoride and Grignard reagent (Scheme 1a). Among them, hydroxyphosphine ligands can combine electron-rich nickel (0) and Lewis acidic magnesium to promote the activation of C-F bond. Ackermann's research group (Isr. J. Chem. 2010, 50, 652.) first used secondary phosphine oxide (SPO) ligands for cross-coupling reactions, which also involved the use of similar bimetallic mechanisms. At the same time, the Ni/Al catalyst synthesized from (chiral) SPO ligand also represents a highly efficient TM/LA bimetallic system, which can be used for C-H activation of Lewis basic substrate (Scheme 1b). Recently, Wang Chen of Shaoxing University and Naohiko Yoshikai Research Group of Tohoku University of Japan designed and developed a new type of Co/Al and Co/Mg bimetallic catalyst synthesized by PSPO, which can be used for site-selective C-H alkylation reaction of azaaromatics and alkynes (Scheme 1c).
(Image source: Angelw. Chem. Int. Ed.)
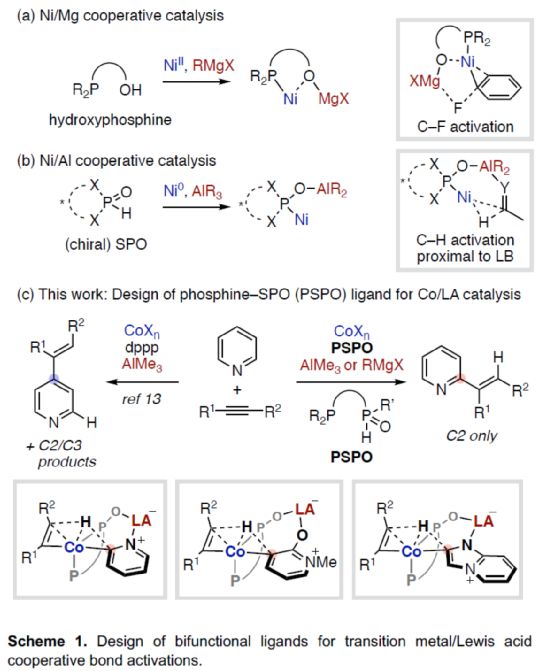
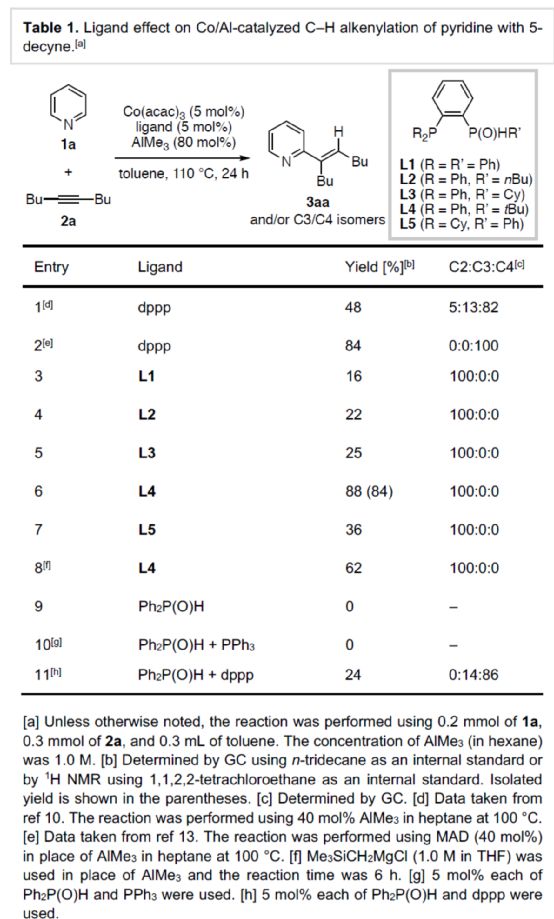
First of all, the author used pyridine 1a and 5-decyne 2a as model substrates to screen the relevant alkylation reaction conditions (Table 1). When Co (acac) 3 (5 mol%) and AlMe3 (80 mol%) were used as metal catalysts and L4 (5 mol%) as ligands, the product 3aa was obtained in 84% yield at 110 oC in toluene solvent for 24 hours, and the ratio of C2: C3: C4 was 100:0:0.
(Image source: Angelw. Chem. Int. Ed.)
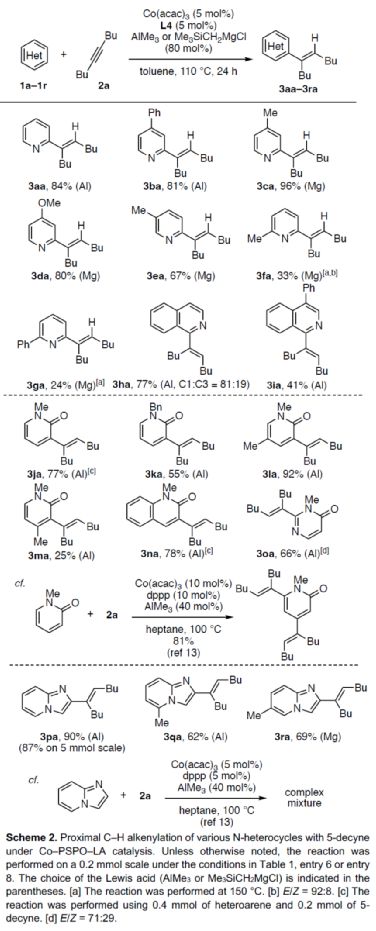
After obtaining the above optimal reaction conditions, the author expanded the substrate range of N-heteroaromatics (Scheme 2). First of all, when the 3 - or 4-position of pyridine contains aryl, methyl or methoxy substituents, it can react smoothly with 2a to obtain the corresponding product 3ba-3ea with a yield of 67-96%. However, when the 2-position of pyridine contains aryl or methyl substitution, the reaction efficiency is significantly reduced, and the corresponding product 3fa-3ga is obtained, with a yield of 24-33%. At the same time, isoquinoline has competitive alkenylation at C1 - and C3 - positions, and the corresponding product 3ha can be obtained with 77% yield, and C1: C3 is 81:19. 4-phenylisoquinoline, which is alkenyled only at the C1 position, can yield the product 3ia with a yield of 41%. Secondly, 1-methyl-2-pyridinone, 1-benzyl-2-pyridinone, 1,5-dimethylpyridinone and 1-methyl-2-quinolone can also react smoothly with 2a to obtain the corresponding products 3ja-3la and 3na in a yield of 55-92%. However, the product 3ja was obtained with only 25% yield of 1,4-dimethyl-2-pyridinone. 3-methyl-4-pyrimidinone can be alkenylated at the C2 position, and the product 3oa can be obtained in 66% yield. It is worth noting that when dppp is used as a ligand, 1-methyl-2-pyridinone can undergo alkenylation reaction at C4 - and C6 - positions simultaneously, and corresponding dienylation products can be obtained with 81% yield. In addition, imidazolo [1,2-a] pyridine derivatives can also be successfully reacted to obtain the corresponding product 3Pa-3ra with a yield of 62-90%. It is noteworthy that when dppp is used as a ligand, imidazolo [1,2-a] pyridine only obtains mixed products during the alkylation reaction. It is more convenient and rewarding to download the chemical plus APP to your mobile phone.
(Image source: Angelw. Chem. Int. Ed.)
Next, the author expanded the substrate range of alkynes (Scheme 3). First of all, symmetric dialkyl alkynes can react with 1p smoothly to obtain the corresponding product 3Pb-3pc with a yield of 82-94%. When 2-heptane reacts with 1p, the alkenylation reaction is carried out at the position with small steric hindrance, and the product 3pd can be obtained with 61% yield, and the r.r. is 2.8:1. For alkynes with significant spatial asymmetry, they can react smoothly with 1p to obtain the corresponding product 3pe-3pj with a yield of 42-91%. Secondly, when 2-heptane reacts with 1a, the C2-position alkenyl product 3ad can be obtained with 72% yield, and the r.r. is 2.0:1. For alkynes with significant asymmetric spatial differences, they can react smoothly with 1a to obtain the corresponding product 3af-3ah with a yield of 70-87%.
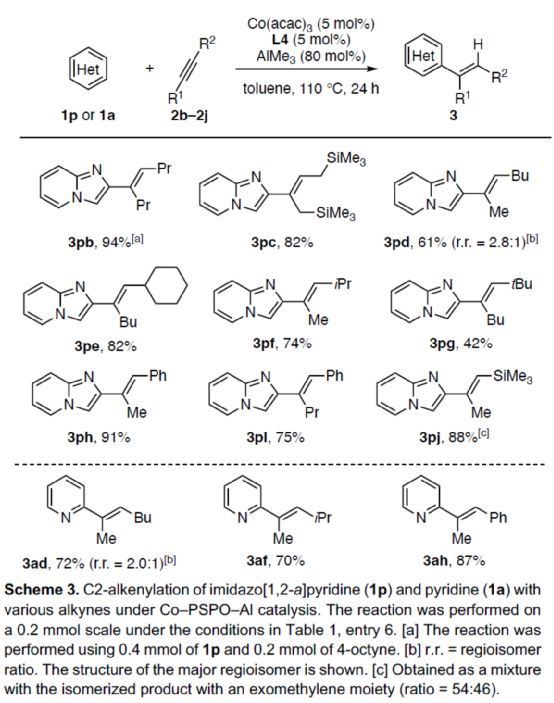
(Image source: Angelw. Chem. Int. Ed.)
At the same time, the author found that if the Co-PSPO-Al and Co-dppp/AlMe3 catalytic system were combined, the dienylation reaction (Scheme 4) could be realized. Therefore, 3pa or 3pf can react smoothly with 2a under the co-dppp/AlMe3 catalytic system to obtain corresponding products 4a and 4b, with a yield of 62-80%.
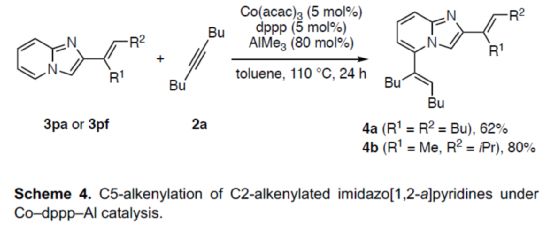
(Image source: Angelw. Chem. Int. Ed.)
In addition, the author studied the reaction mechanism (Scheme 5). The cross experiment shows that the transfer of pyridine and hydrogen atoms takes place in a single molecular way (Scheme 5a). Competitive H/D KIE experiments showed that C-H bond cleavage could irreversibly convert pyridine substrate into catalytic intermediate (Scheme 5b). The H/D KIE experiment of parallel reaction shows that the speed determination step of alkenylation can be changed according to the reaction conditions, and is not fixed in a specific step (Scheme 5c).
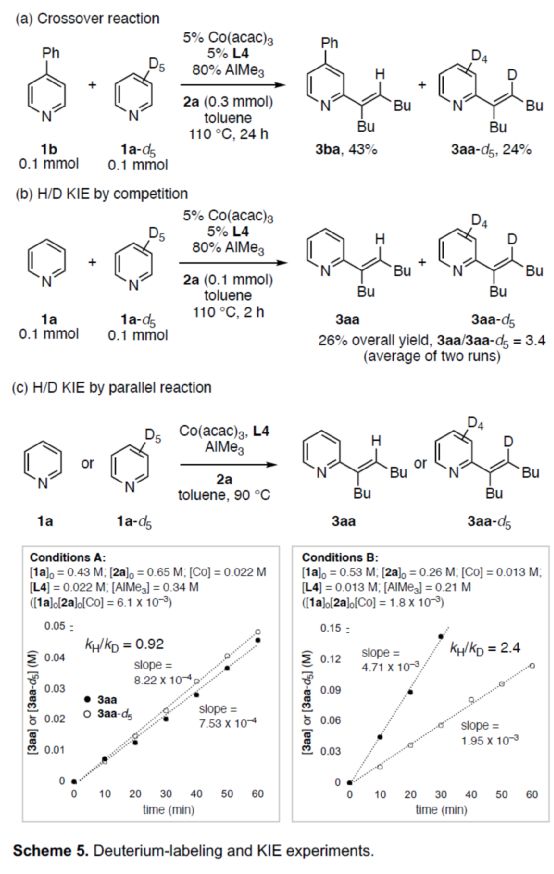
(Image source: Angelw. Chem. Int. Ed.)
Based on the above research and relevant DFT calculation, the author proposed a reasonable catalytic cycle process (Scheme 6). First of all, a more stable catalytic intermediate, namely the triplet (CP1_t), was formed in the reaction and_ T and CP3_ TIn equilibrium. Subsequently, the cleavage of pyridine C2-H bond was carried out smoothly through ligand-ligand hydrogen transfer (LLHT) transition state (TS1_s) in the singlet state to generate complex INT1_ s。 INT1_ S via TS2_ S transition state is rearranged to produce a more stable complex INT2_ s。 INT2_ S via TS3_ S transition state is reduced and eliminated to form complex INT3_ s. It can be further converted into a more stable INT3_ t。 Finally, the target product can be generated and the active catalytic intermediate CP1 can be regenerated after the bond breaks_ t。 Interestingly, this is in sharp contrast to the mechanism of catalytic C-H alkylation of formamide by Co-dppp/AlMe3, in which the reduction elimination is preferentially carried out in the triplet state.
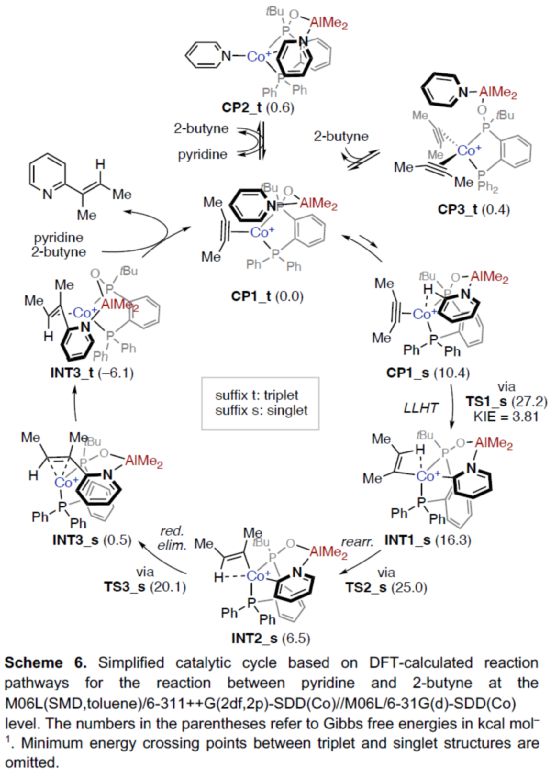
(Image source: Angelw. Chem. Int. Ed.)
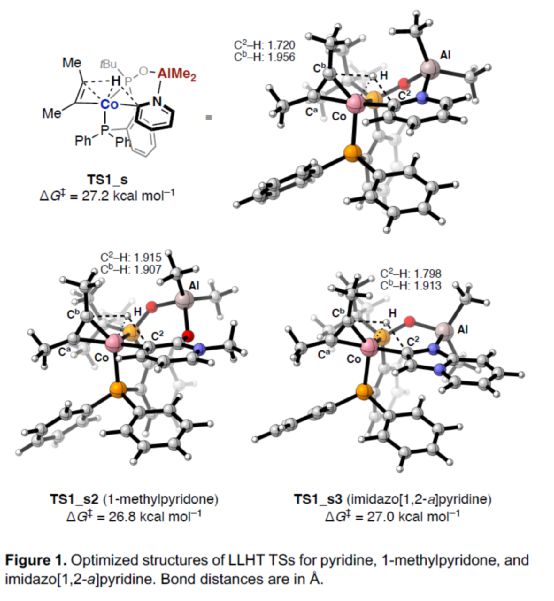
In addition, the author also optimized the structure of TS in the LLHT process of pyridine, 1-methylpyridinone and imidazolo [1,2-a] pyridine (Figure 1). The research shows that in the LLHT process, alkynes with different sizes of substituents are more likely to accept hydrogen atoms near the larger substituents to avoid the spatial repulsion between them and phosphine-co units, thus selectively forming C-C bonds on alkynes with less steric hindrance.
(Image source: Angelw. Chem. Int. Ed.)
summary
Wang Chen of Shaoxing University and Naohiko Yoshikai Research Group of Tohoku University in Japan designed and developed a new type of Co/Al and Co/Mg bimetallic catalyst synthesized by PSPO, which can be used for the near-end selective C-H alkylation of Lewis basic heteroaromatic compounds (such as pyridine, pyridone and imidazolo [1,2-a] pyridine). The effectiveness of PSPO ligands highlights the design concept of nickel and cobalt orthorhombic ligands, in which the chelation of bidentate phosphine is crucial for the synergistic effect of cobalt and Lewis acid to promote the current type of C-H activation. DFT study proved the universality of LLHT mechanism. It is worth noting that KIE research shows that a set of reaction conditions cannot be used to judge whether the C-H bond fracture is involved in the rate-determination step.
Statement: Our company only publishes or reprints this article for the purpose of transmitting and sharing more information, and does not mean to agree with its views or confirm its description. If the source label is incorrect or infringes your legitimate rights and interests, please contact us with the ownership certificate, and we will correct and delete it in time. Thank you.
Contact: Emma Chen
Phone: +8618791163155
Tel: +8618791163155
Email: 18791163155@163.com
Add: Room 403,Building 8,West Life Science and Technology Park,Keyuan 4th Road,Xixian New District,Xi'an City,Shaanxi Province
We chat
